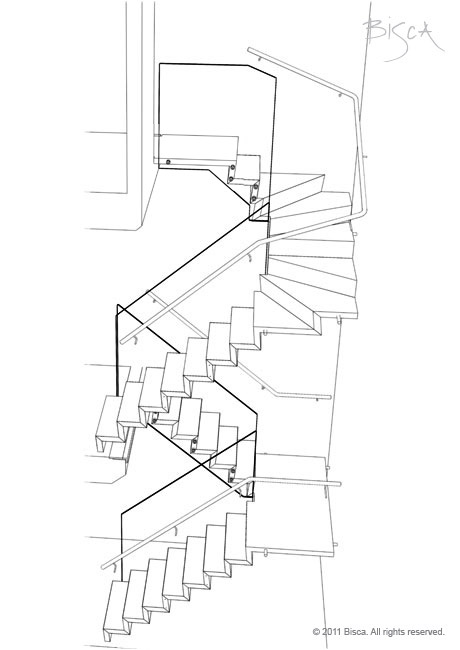
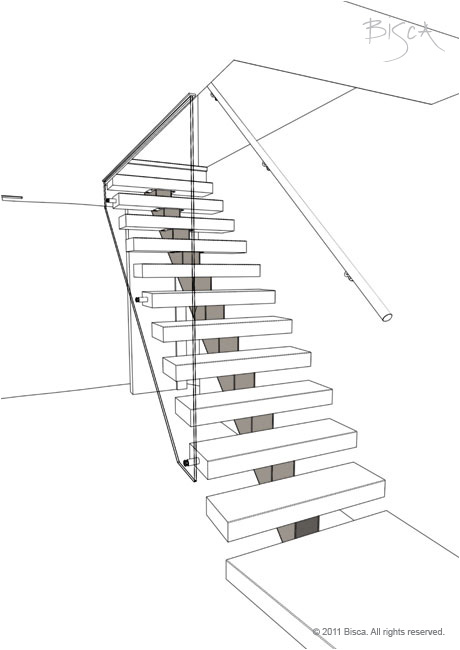
Cantilevered Staircase
Staircase with no visible support. Treads and risers are supported from one side only, usually via a hidden stringer in the wall.
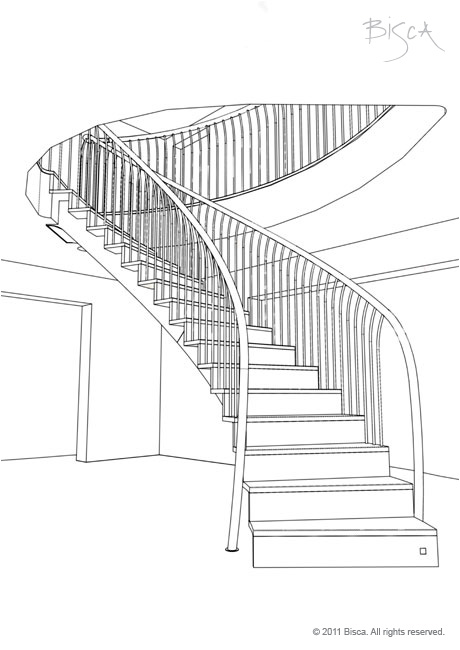
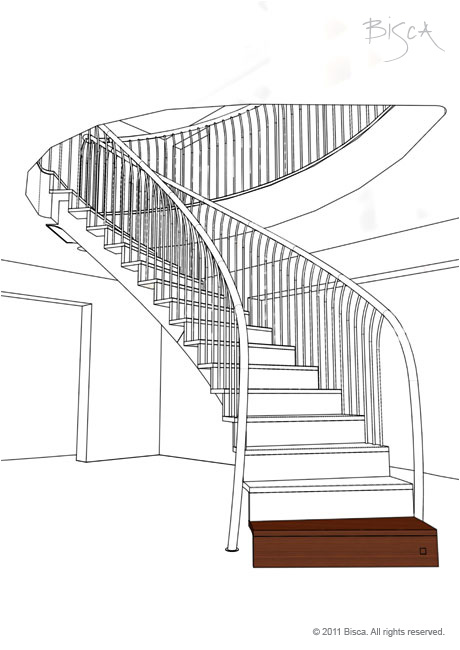
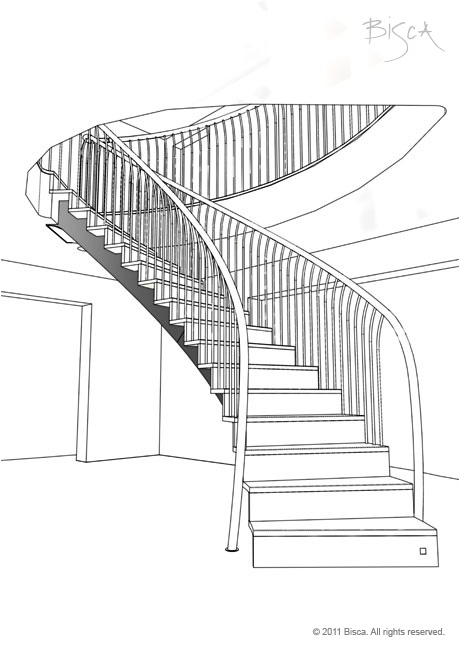
Helical Staircase
Can assume oval, elliptical or curved plan. The term helical descries the shape of the stair and can be free floating in a space or built alongside a wall.
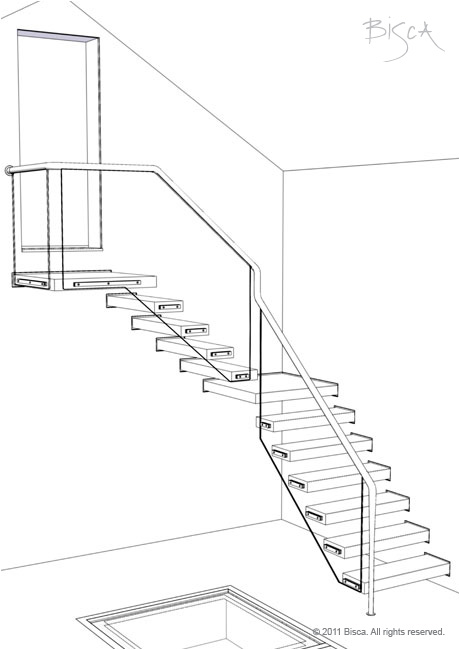
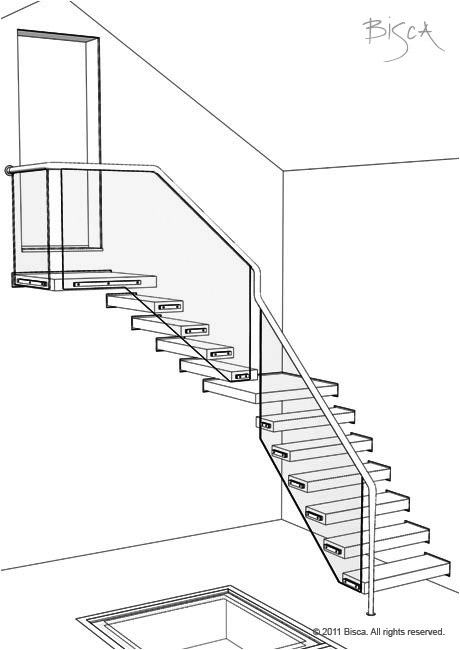
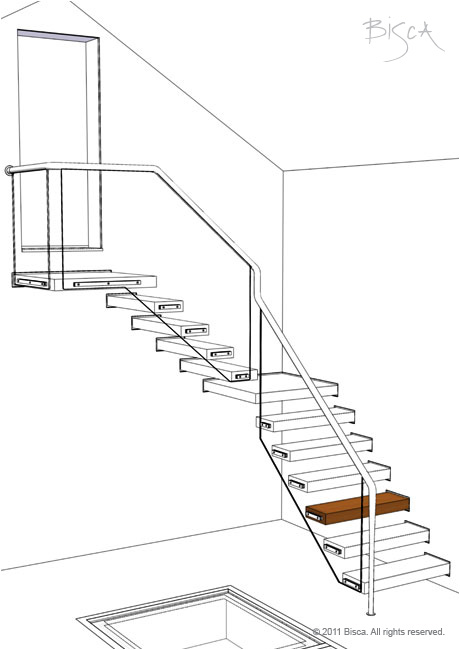
Multi-Flight Staircase
A staircase that connects more than 2 floors.
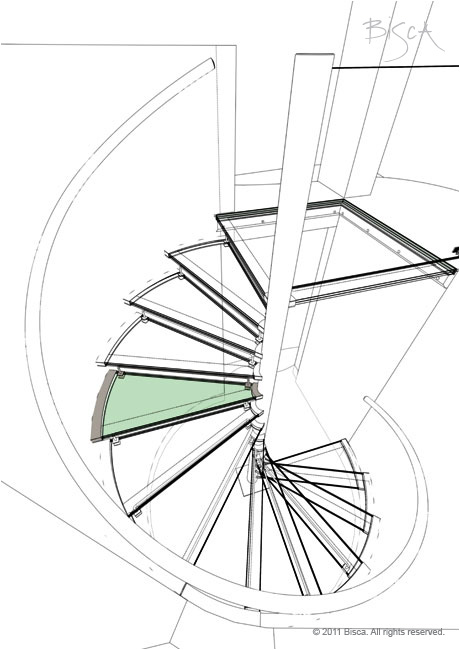
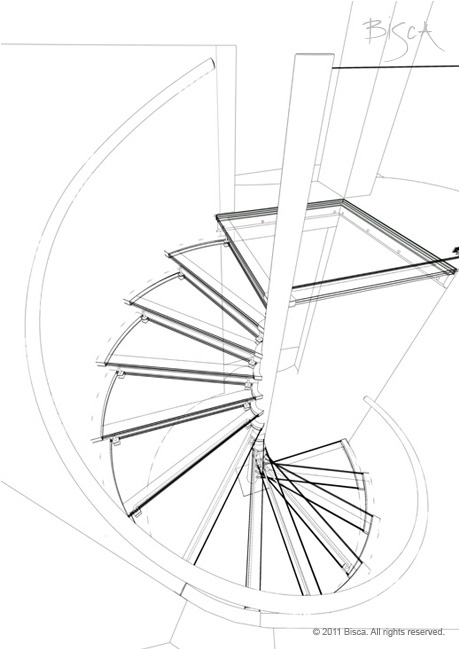
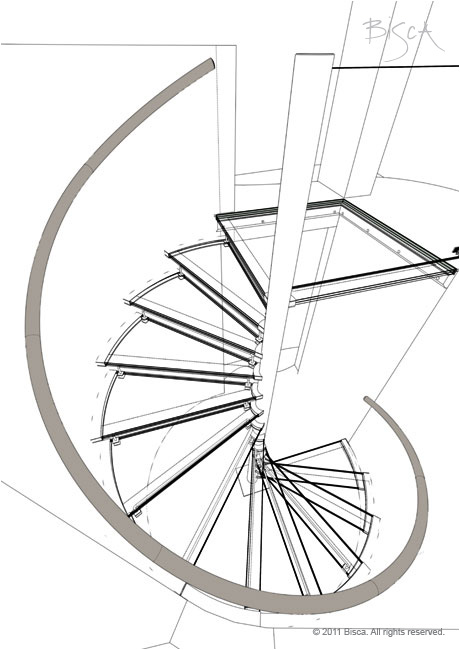
Spiral Staircase
A stair that winds round a central pole and assumes a circular stairwell.
Straight Staircase
A straight flight connecting 2 levels; can also be against a curved wall; straight stairs have no turns.
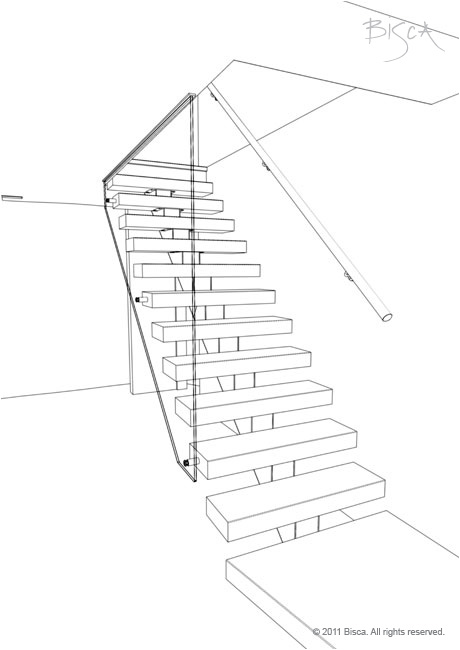
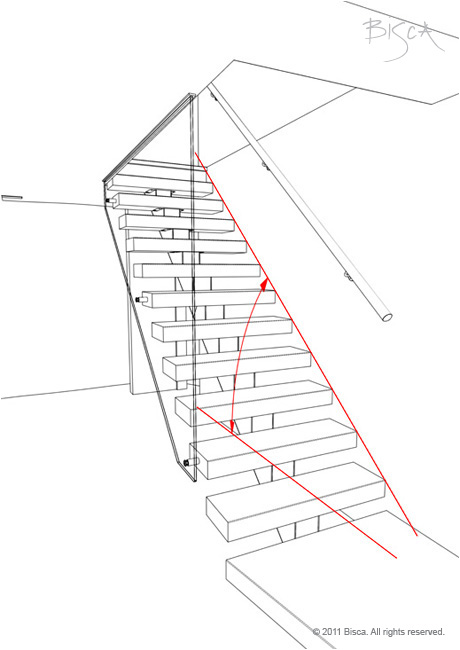
Angle
The angle at which a stair rises, measured between the pitch line and the horizontal floor level at the foot of the stair. The maximum pitch a stair can be is 42 degrees.
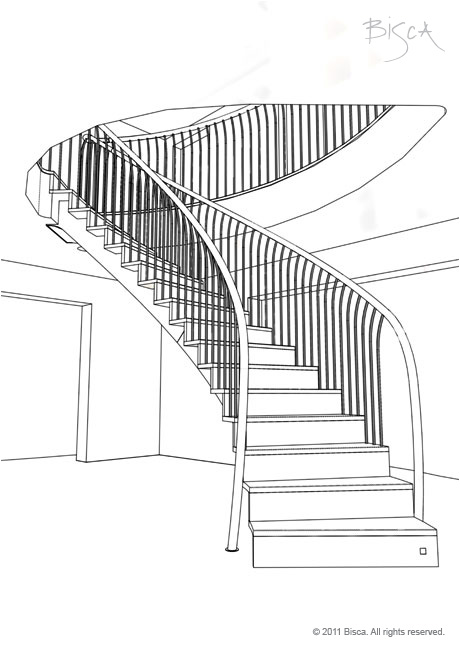
Baluster
A vertical member used as the infill in a balustrade. Can take on a variety of different shapes and forms.
Balustrade
A barrier or containment at the side of a stair, landing, floor edge or balcony to provide protection from falling. Usually comprises of: an infill element which, for example, could be a glass panel or a series of balusters; a handrail and one or more newels.

Bannister
Rail that runs along the edge of a staircase or balcony to be grasped for support. Usually fixed as part of the balustrade or independently to a wall.
Bezel
Slim, usually stainless steel component used to finish connections into walls and floors.

Flight
The part of a stair between floor levels that has a continuous series of steps. A single flight can have one or more landings.
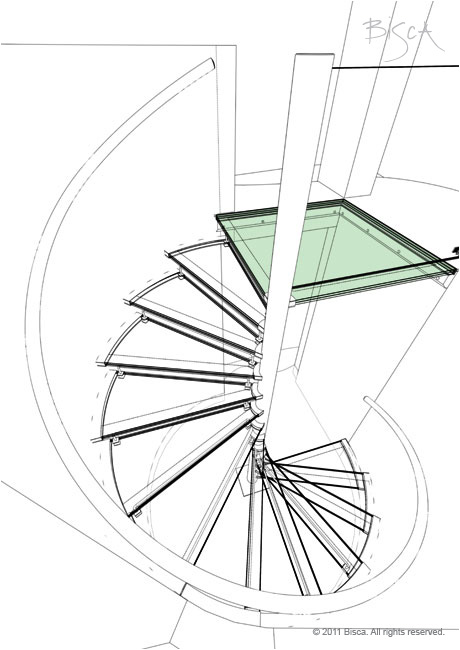
Glass - Annealed
Glass that does not have the internal stresses and therefore added strength of toughened or heat treated glass. If broken will crack into shards.
Glass - Clamp
Stainless steel component used for fixing glass balustrade panels to treads/landing edges.

Glass - Heat strengthened
Glass that has been heat treated, much in the same way as toughened glass to increase strength, but not to the same extent. Heat strengthened glass is stronger than annealed glass but not as strong as toughened. If broken it will crack into shards rather than shatter.

Glass - Laminated
Glass panel manufactured by bonding two or more layers together typically with Polyvinyl butyral (PVB), a strong binding resin or Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA).

Glass - Low Iron
Glass with a reduced green tint.
Glass - Standoff
Stainless steel component used for fixing glass balustrade panels to treads/landing edges.

Glass - Tempered
Glass that has been heated and rapidly cooled to create balanced internal stresses to give it increased strength. If broken toughened glass will shatter into small squares.
Glass - Toughened
Glass that has been heated and rapidly cooled to create balanced internal stresses to give it increased strength. If broken toughened glass will shatter into small squares.

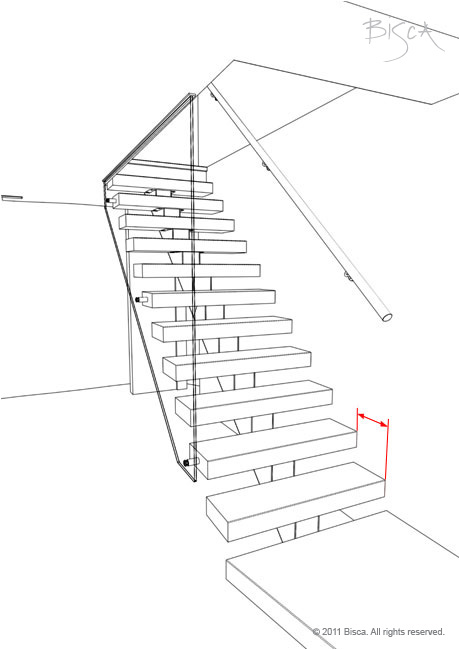
Going
The horizontal dimension from the front of a tread to the front of the tread above. The dimension can be taken from face of riser to face of riser or tread nose to tread nose. The going must remain constant throughout a flight.
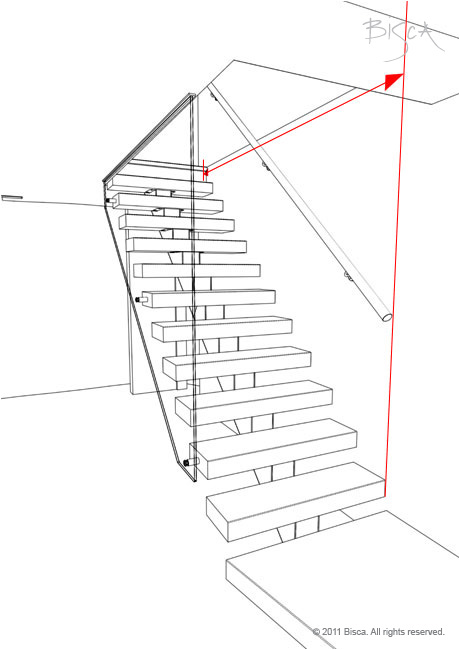
Going - Total
The horizontal distance between the face of the first and last riser or the first and last tread nose in a flight. Should equal the total of all goings.
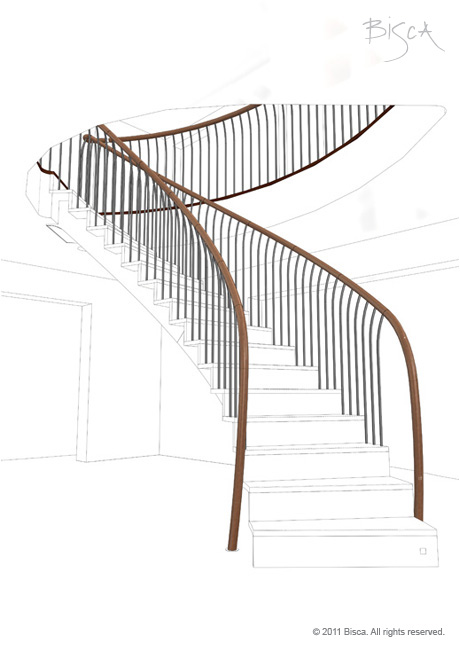
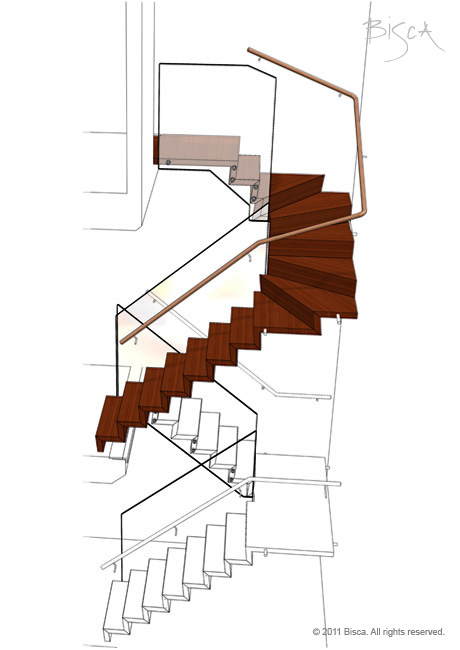
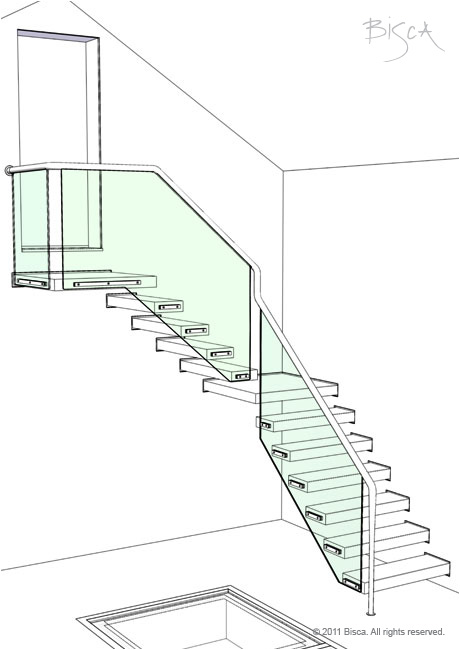
Handrail
Rail that runs along the edge of a staircase or balcony to be grasped for support. Usually fixed as part of the balustrade or independently to a wall.

Landing - Half
A landing within a stair used to turn it through 180 degrees.
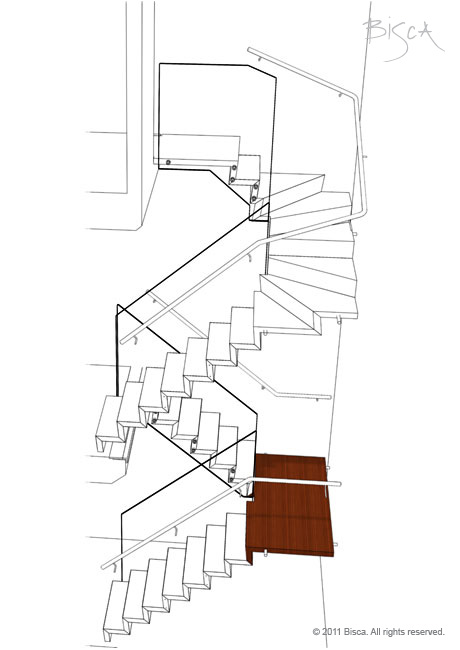
Landing - Intermediate
A landing within a stair.
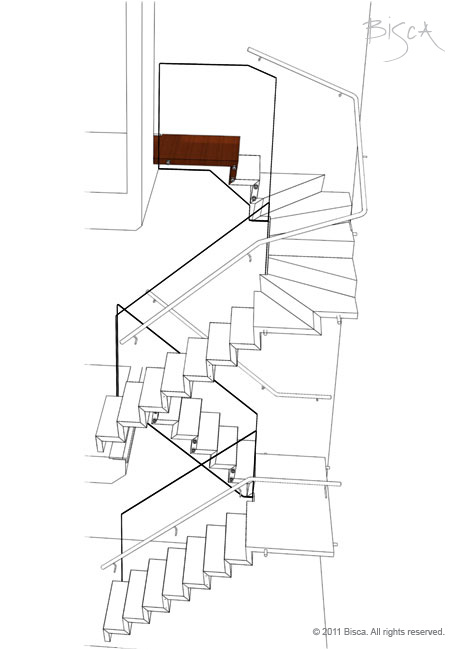
Landing - Quarter
A landing within a stair used to turn it through 90 degrees.
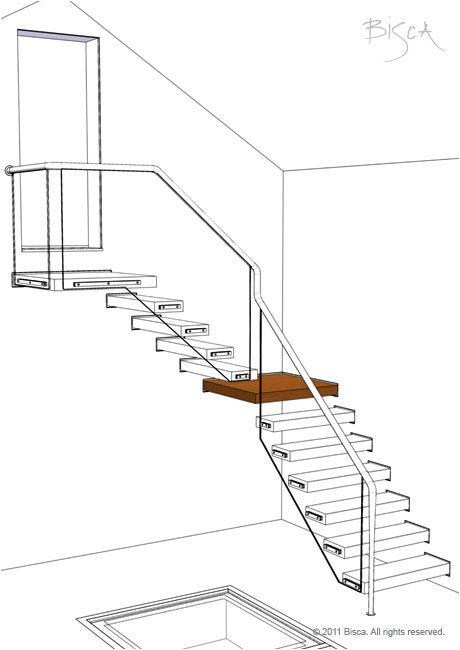
Newel
The post found at; the beginning of, or point of change in, a balustrade. Newels provide structural stability to the balustrade, a connection to the floor, and are often integral to supporting the handrail. Not always necessary as a structural element a newel can be used purely as a decorative feature to punctuate transitions within a balustrade and highlight areas of a stair.
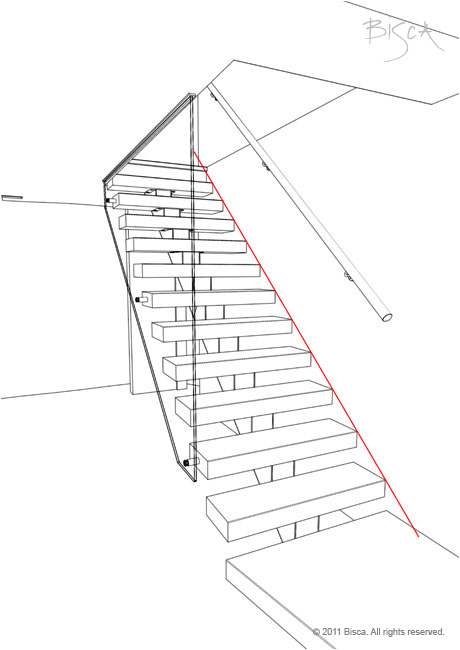
Pitch
The angle at which a stair rises, measured between the pitch line and the horizontal floor level at the foot of the stair. The maximum pitch a stair can be is 42 degrees.

Pitch line
The imaginary line that runs diagonally through the front edge or tread nose of every tread in a stair. It is used to measure the pitch of the stair.
Railing
A barrier or containment at the side of a stair, landing, floor edge or balcony to provide protection from falling. Usually comprises of: an infill element which, for example, could be a glass panel or a series of balusters; a handrail and one or more newels. The word railing is more commonly used to describe an external feature.

Rake
The angle at which a stair rises, measured between the pitch line and the horizontal floor level at the foot of the stair. The maximum pitch a stair can be is 42 degrees.

Rise
The individual height of a step, the vertical dimension between consecutive treads. The rise must remain constant throughout a flight.
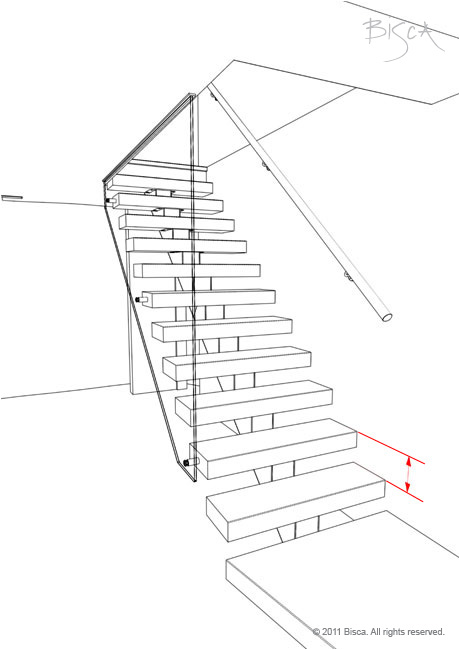
Rise - Closed
A staircase with a closed rise has risers.
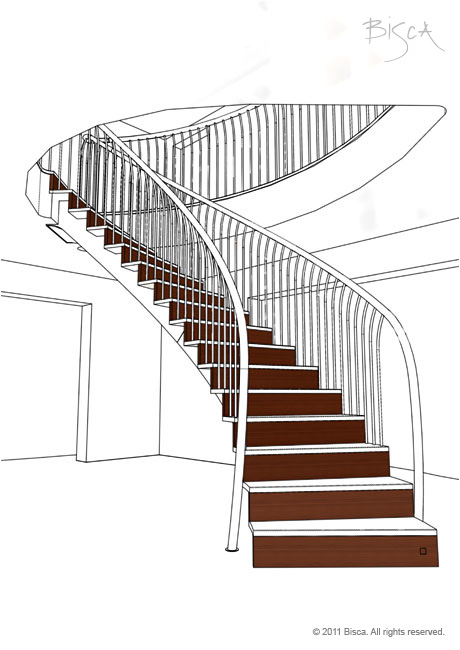

Rise - Open
A staircase with an open rise has no risers so there is a clear gap between each tread.
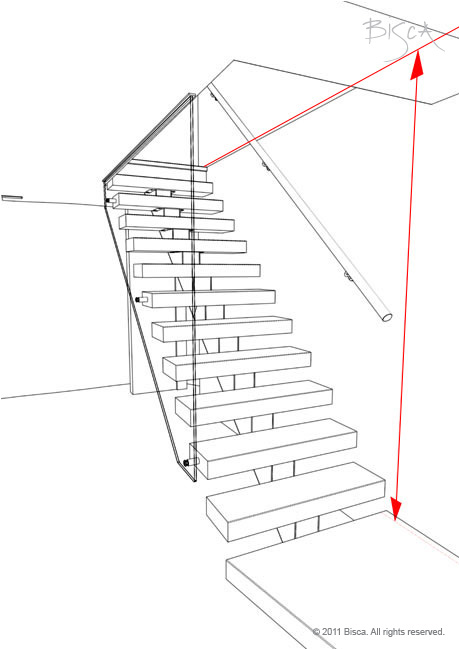
Rise - Total
The vertical distance between the floors or landings connected by a flight. Should equal the total of all risers in a flight.
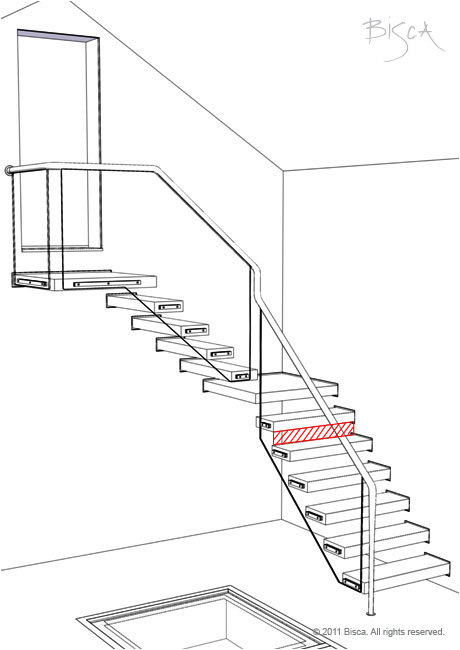
Riser
The vertical part of a step; closes the gap between treads.
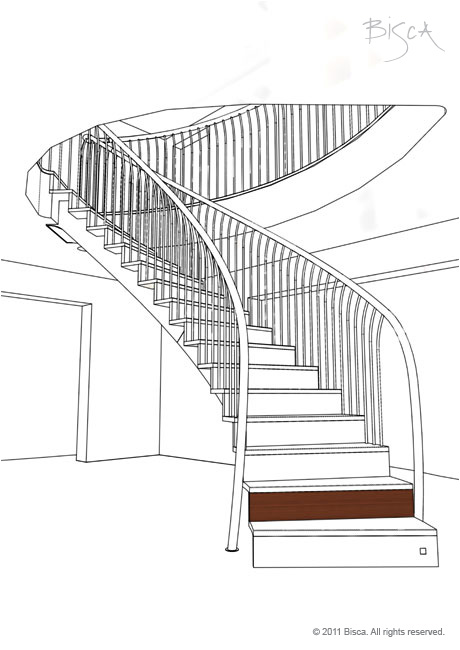
Spindle
A vertical member used as the infill in a balustrade. Can take on a variety of different shapes and forms.

Spine
An alternative means of support to a stringer, a spine also runs parallel with the pitch of the stair but supports it from the underside as opposed to the edges.
Step
Tread and riser combined.
Stringer
Common staircase components that runs parallel with the pitch of a stair. A stair can have a single stringer (on one side) or double stringers (on both sides). Stringers add structural stability to treads and risers and tie them together. A Full Stringer supports treads from the outside and covers the ends of the treads. A Cut Stringer is also known as a "saw-tooth" stringer - the top edge is ‘cut’ to follow the shape of the treads and usually supports treads from below, leaving the end of the tread itself exposed.
Tread
The horizontal part of a step, the surface that you stand on.
Tread Nose
The front edge of a tread that protrudes over the tread below. The dimension of the protrusion must remain constant throughout a flight in order to preserve the going.
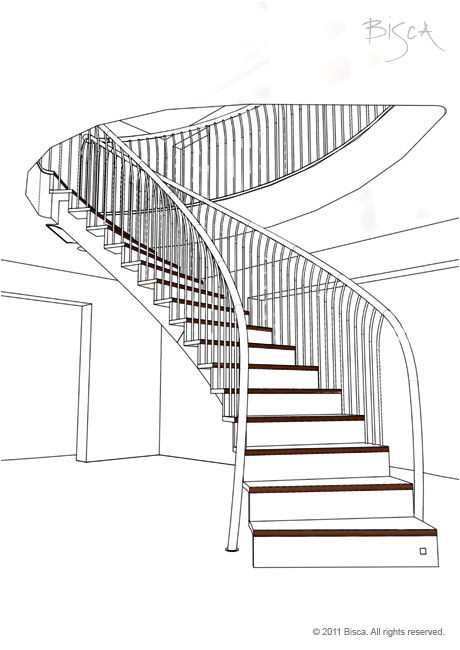

Upright
A vertical member used as the infill in a balustrade. Can take on a variety of different shapes and forms.

Winder
Radial step used to make a flight gradually change direction. The nose of a winder is not parallel with the nose of the step or landing above it.